Wnt program
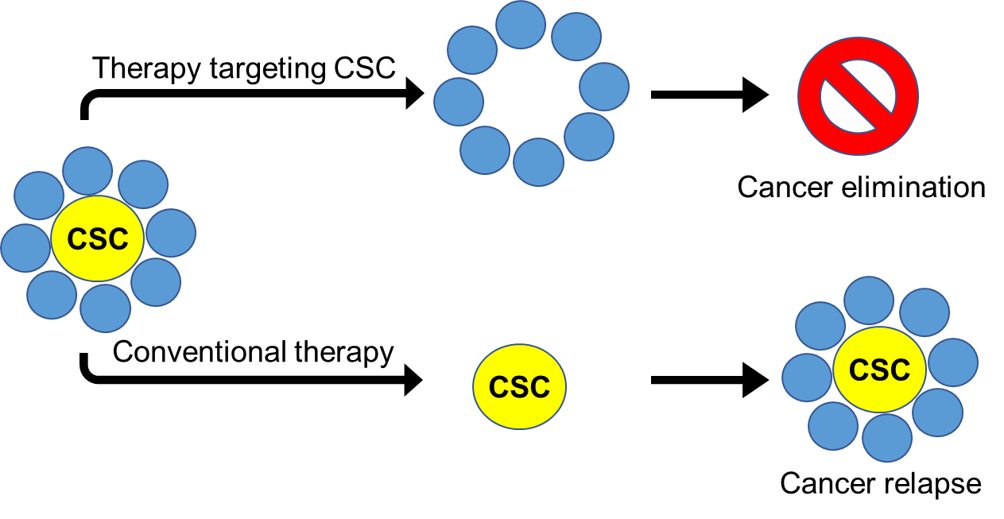
Wnt signaling is a fundamental pathway regulating stem cell during development and cancer stem cells (CSCs) during carcinogenesis. The minimal residual disease remaining standard chemotherapies often enriches for Wnt-responsive CSCs, leading to relapse. Therefore, by targeting Wnt, we are targeting CSCs in Wnt-driven cancers, such as colorectal cancer (CRC).
In the absence of Wnt ligands, beta-catenin is degraded constitutively, through a destruction complex consisting of Casein Kinase 1 alpha (CK1alpha), GSK3, APC, and AXIN. The pathway is activated by the binding of a Wnt-protein ligand to a Frizzled family receptor, which passes the biological signal to the inside of the cell to stabilize beta-catenin (ligand-dependent) signaling. Mutations in APC, a key component of the destruction complex or beta-catenin, result in ligand-independent stabilization of beta-catenin. Both mechanisms of activation result in nuclear accumulation of beta-catenin and subsequent activation of the WNT transcriptional program to support CSCs.
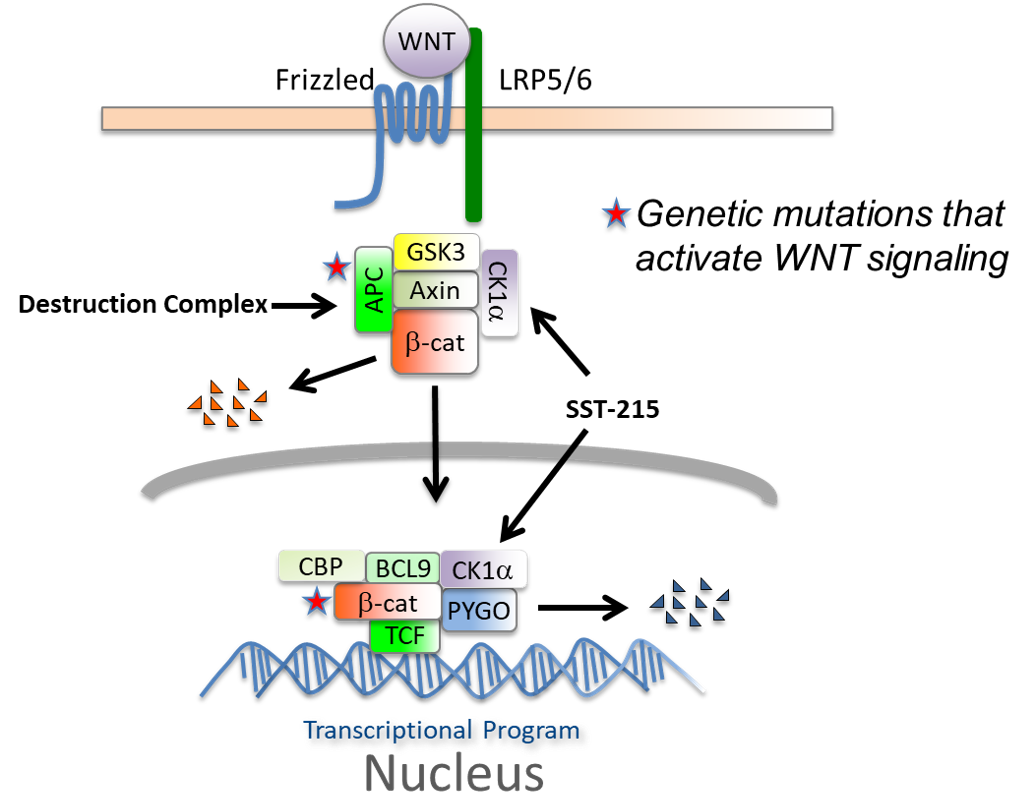
SSTI discovered and developed of a novel class of small molecule activators of CK1alpha, SST-215 series compounds, that inhibit the Wnt pathway at two critical nodes, reducing levels of:
- A) the cytosolic Wnt effector, beta-catenin
- B) the nuclear transcription regulator Pygopus2 (PYGO)
SST-215 and more advanced analogs are first in-class Wnt pathway inhibitors:
- A novel mechanism of action and cellular target
- Potent inhibitors of Wnt signaling (nanomolar IC50s in cell based assays)
- Efficacious in eradicating CRCs in cell culture and in vivo
- Minimum on-target toxicity in the gastrointestinal tract, in contrast to WNT inhibition by tankyrase inhibitors (TANKi).
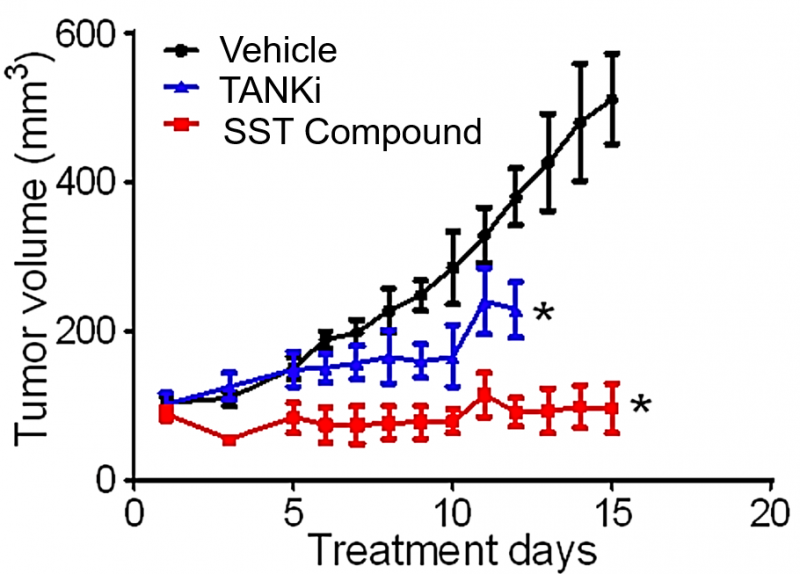
SST Compound is effective in eradicating CRCs in vivo. Nude mice bearing the human CRC xenografts, SW403, were dosed with vehicle, SST Compound, or a TANKi over 15 days. The TANKi study arm was terminated early due to overt toxicity.
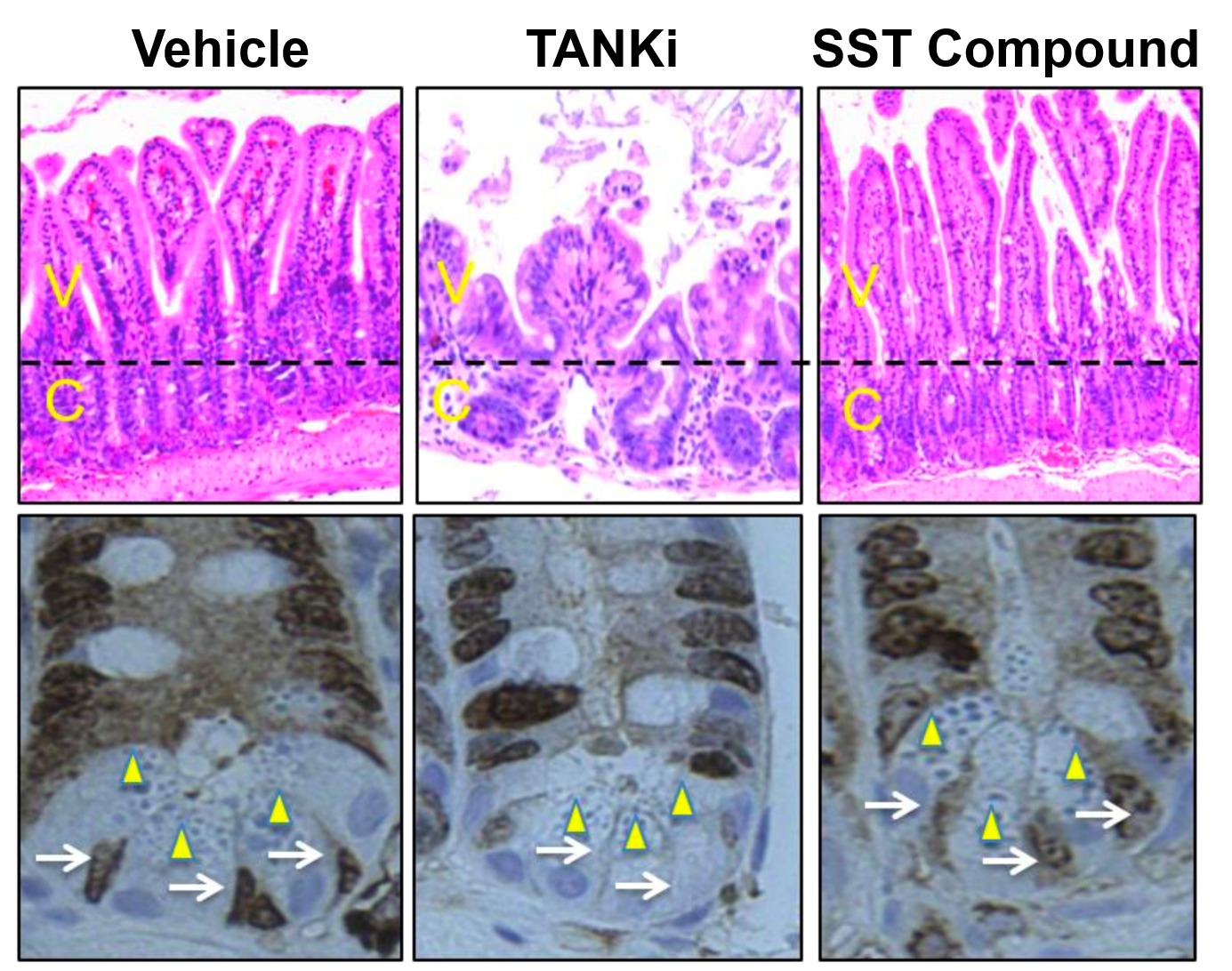
Minimal toxicity associated with SST Compound treatment. Top panels. H&E staining of the intestinal crypts shows disruption of the normal architecture with TANKi’s and not with SST Compound. C = Crypt. V = Villi. Bottom panels. Immunostaining for a cell proliferation marker (Ki67) shows the presence of Paneth cells (arrowhead) and stem cells (arrow) after vehicle and SST Compound treatment but not after TANKi treatment.